Astronomy : Importance
From the measured dates by the observation of Venus transit it is possible to calculate the distance Sun - Venus (astronomical unit, further just AU). In different places on the Earth, we record exact moments of the second and the third contact and then, by the assistance of the parallax and triangulation method we calculate the AU. However, it is necessary to observe the phenomenon from minimally two places. The further the places are from each other, the more exact the result will be. Because of this, many adventurous expeditions were realized in the past - see history of VT. The exact determination of the times is complicated by so-called black-drop efect. It is a dark area connecting the Sun's edge with the transiting Venus' edge at the beginning of the second contact and a moment before the third. The efect is caused by light refraction in a very thick Venus' atmosphere, but it was observed by the transit of Mercury, as well. From this fact, the astronomers rightly determined that Venus was surrounded by the atmosphere.

Black-drop efect
Triangulation method
Triangulation serves for determining the distance of the object and the observer. It is a condition to observe it from two places (A, B), at the same time, measure the angle beneath we see it(alpha, beta) and know the distance between the observers (d). From these data we can count the distance us-the object(y, y1).
There is described the calculation itself for those interested:
We will divide the distance between the observers' places by a perpendicular fallen from the object to the surface (y) into two pieces (a, d-a). This perpendicular distance can be expressed by the assistance of both angles:
tg alpha= y/a y= tg alpha *a tg beta= y/(d-a) y= tg beta* (d-a)
Now we can put together a linear equation with one unknown:
y=y tg alpha *a=tg beta* (d-a)
From this equation we express the unknown a:
a=(tg beta *d)/ (tg alpha+tg beta)
And now, when we know the angle and a side in a right-angled triangle, we can count another arbitrary side , possibly the distance between the object and the observer A (X):
cos alpha= a / x x= a / cos alpha
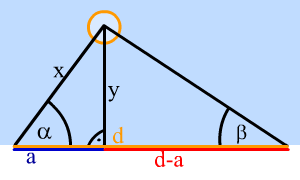
for illustration ther's an image
The application of triangulation method on the calculation of the astronomical unit is a bit more difficult, but the basic principle is the same as in the example. This simplified method cannot be used for the calculation of AU, because The Sun is too far from the Earh and so we cannot measure the angles with sufficient precision.