Transit : Course
By observation of the Sun you must realize wheter you are observing by a naked eye or by a telescope with parallactic montage. Of course, the phenomenon runs in the same way, there is just a difference in the projection.
If you will use no tool for the observatio of the Sun, or if you will use just a telescope, which is fixed on a fast tripod and which does not invert the image, you will look at the Sun still from a different angle with increasing time. This is caused by the Earth's rotation - the Sun, with regard to the stars, is oriented almost in the same way, but our Earth swivels relatively fast. So, if you "mark" the upper point of the Sun disc at 8 o'clock, at 10 o'clock this point will not be exactly up (towards the horizon).

Parallactic montage, however, equalizes the revolving motion of the Earth, because it has one axis parallel with the Earth's axis. So, if you "mark" a point on the Sun disc in a telescope with such montage, after a few hours this point will be still in the same place.
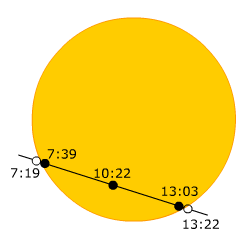
- 1st contact - the bodies touch themselves from the outside. In this moment, the body transiting over the Sun is difficultly observable, because we see (like do not see) only the reverse side, which does not cover the Sun disc yet.
- 2nd contact - inner contact of the bodies: In this moment we can already see the transiting body.
- Maximal phase - the moment, when the bodies cover themselves the most. In this case, it is the phase when Venus is exactly in the half of its track over the Sun.
- 3rd contact - analogy of the 2nd contact, but the bodies distance themselves.
- 4th contact - the last touch of these two bodies. In this moment, Venus stops being observable.
These phases occur by Venus transit over the Sun disc 8th June 2004 at this time:
| Event | Time CEST |
| 1st contact | 7:19 |
| 2st contact | 7:39 |
| Maximal phase | 10:22 |
| 3st contact | 13:03 |
| 4st contact | 13:22 |